Email-Automation – The Mechanism – Die Basics
Welcome to the first installment of our email automation blog series! In this first post, we’ll dive into the basics and take a look at the three control elements: trigger, story and branching.
Triggers: The triggers for automated emails
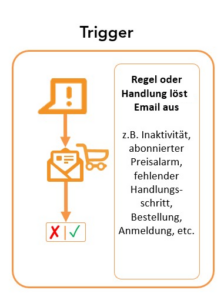
Triggers are the key component of every (email) automation. You define when an email is sent based on certain conditions or actions. A trigger can be a user action such as subscribing to a newsletter, but also reaching or falling below a certain key performance indicator (KPI). For example, an email can be triggered when a user becomes inactive based on a dynamic score that evaluates user activity.
Other examples of triggers include:
- A customer’s birthday or anniversary
- Abandoning a product in the shopping cart without purchasing
- Registering for a webinar or event
Story: The route of activities and triggers

The story is the sequence of activities and triggers that represents a thoughtful journey for the user. A classic example is the onboarding route, which helps a user get started with a product or service and leads them through various processes until the final onboarding. This route can also serve as a tutorial that familiarizes the user with the product or service at regular intervals.
Other examples of story elements include:
- A welcome series for new subscribers
- A re-engagement campaign for inactive users
- A product usage route to introduce new features
Branching: The personalized interaction
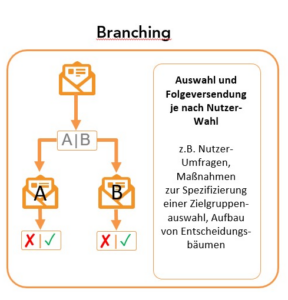
Branching makes it possible to create different paths in email automation depending on the user’s actions or preferences. Similar to “if-then” statements, branching offers options in which the user has an option to act and, depending on their choice, a corresponding answer or reaction is given.
Examples of branching are:
- Choosing between different product offerings based on previous purchases
- The selection of topic areas for personalized newsletters
- Deciding between different actions in a survey or vote
Conclusion
The basics of email automation are crucial to building an effective and customer-focused marketing strategy. Triggers, stories and branching form a logical framework for developing automated email campaigns that offer users relevant and engaging content.
By using triggers correctly, companies can automatically determine the right time to send emails and thus achieve a higher engagement rate. The story makes it possible to create a cohesive and purposeful journey for users, whether onboarding new customers or launching new products. Finally, branching opens up opportunities for personalized interactions that make it possible to respond to users’ individual needs and preferences.
By understanding and effectively using these basic principles of email automation, companies can not only increase the efficiency of their marketing process, but also improve customer satisfaction and retention.
#EmailAutomation #MarketingAutomation #Trigger #Story #Branching #Customer Centricity